Introduction:
Napoleon Bonaparte, a towering figure in history, was a military and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution. Born in Corsica in 1769, he rapidly climbed the ranks of the military, eventually declaring himself Emperor of the French in 1804. Renowned for his military genius and the Napoleonic Code, his legacy is a complex tapestry of triumphs and controversies. This study dives into the dual nature of his impact, exploring the positive reforms and enduring contributions alongside the darker shadows of authoritarian rule.
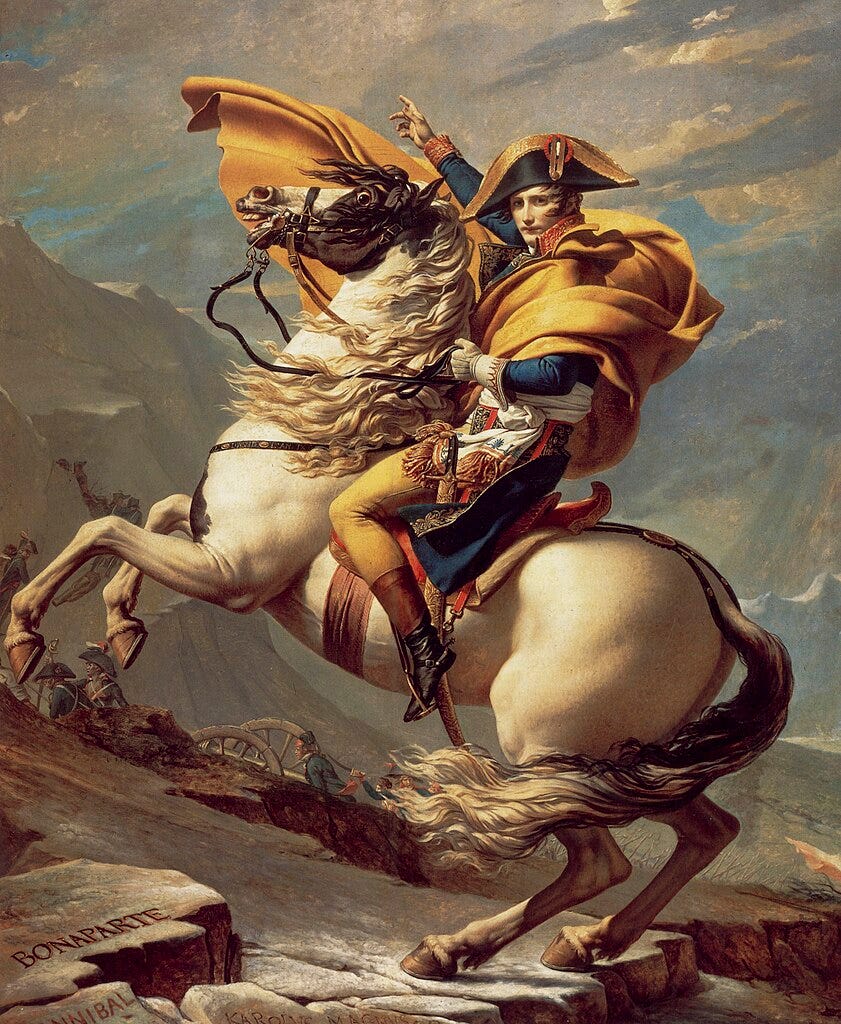
To set the stage for our exploration, envision Napoleon's audacious crossing of the Alps, immortalized in the iconic painting Napoleon Crossing the Alps painted by the French artist Jacques-Louis David between 1801 and 1805.
This image captures the indomitable spirit of a leader ascending to new heights, both literally and figuratively. Brace yourself for a journey through history, where the enigmatic Napoleon unfolds in both light and shadow, inviting reflection on the intricate threads woven into his legacy.
I. Rise to Power:
Napoleon's journey to power began in the rugged landscapes of Corsica, where he was born in 1769. His early life was marked by an intense ambition and a keen interest in military strategy. Commissioned as an artillery officer in the French army, he swiftly distinguished himself during the tumultuous years of the French Revolution. The turning point came in 1799 when, as First Consul, he orchestrated a brilliant coup d'état, consolidating his influence and sidelining the existing government.
In 1799, Napoleon Bonaparte orchestrated a pivotal event in French history known as the Coup of 18 Brumaire. At this time, France was grappling with political instability following the radical phase of the French Revolution. The existing government, known as the Directory, faced internal strife, economic challenges, and external threats.
Seeing an opportunity to seize control and bring stability to the nation, Napoleon, then a successful military commander, collaborated with like-minded politicians, including Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès. Together, they devised a plan to overthrow the Directory and establish a more centralized form of government.
On November 9, 1799 (18 Brumaire in the French Republican calendar), the coup unfolded. Napoleon, as First Consul, played a key role in executing the plan. The coup resulted in the dissolution of the Directory and the establishment of the Consulate, with Napoleon as the First Consul, effectively concentrating power in his hands.
Video Citation:
Title: Napoleon's Bloodless Coup
Creator: https://m.youtube.com/@HISTORY
Published: April 2019
This event marked a turning point in Napoleon's ascent to power. It showcased not only his military acumen but also his political astuteness. The Coup of 18 Brumaire laid the foundation for Napoleon's subsequent rise to Emperor, symbolizing a shift from the revolutionary chaos of the Directory to a more stable, albeit authoritarian, phase in French governance.
Napoleon's military prowess shone brightly in the Italian and Egyptian campaigns, where he demonstrated a mastery of tactics that earned him admiration and loyalty. The Battle of Marengo in 1800 stands as a pivotal moment, solidifying his position and paving the way for his ascent to power. A string of victories, including Austerlitz in 1805 and Jena-Auerstedt in 1806, showcased his strategic brilliance, establishing him as a formidable military leader.
Amidst these triumphs, Napoleon skillfully navigated the complex political landscape. In 1804, he crowned himself Emperor, symbolizing the shift from revolutionary chaos to a more stable, albeit authoritarian, rule. This rise to political prominence was marked by a blend of military genius and political acumen, setting the stage for an era defined by his ambitious vision and quest for European dominance.
For a more in-depth exploration of Napoleon's Rise to Power, you may find this article from World Atlas insightful: The Rise to Power and History of Napoleon Bonaparte.
II. Military Triumphs:
Napoleon's military triumphs stand as pillars of his legacy, showcasing his strategic brilliance and innovative tactics that forever altered the course of European warfare. The Italian Campaigns of the late 1790s marked his initial ascent, with victories in battles like Lodi and Arcola, demonstrating his ability to outmaneuver opponents and capitalize on battlefield opportunities. (source, Robert Wilde, ThoughtCo, Apr. 5, 2023).
The Battle of Marengo in 1800 stands as a masterpiece of Napoleon's tactical genius. Faced with a challenging situation, he executed a brilliant maneuver, leading to a decisive victory against Austrian forces. This triumph solidified his position and paved the way for the establishment of the Consulate (source)
In 1805, the Battle of Austerlitz unfolded, earning Napoleon the title of "Master of the Battlefield." His strategic acumen was on full display as he outmaneuvered the combined Russian and Austrian forces. The success at Austerlitz further bolstered his reputation as a military prodigy.
The year 1806 witnessed the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, a testament to Napoleon's flexible and innovative tactics. Employing a combination of fast-moving infantry and artillery, he secured a resounding victory over Prussian forces. This battle showcased his ability to adapt to different terrains and capitalize on the strengths of his armies.
For a detailed account of the Jena–Auerstedt campaign order of battle, you can explore the comprehensive information available on Wikipedia.
Additionally, a vivid depiction of an incident from the battle is captured in the painting "Emperor Napoleon at Jena" by Horace Vernet. The artwork illustrates a moment where, as the emperor ordered a general attack, a guardsman took off his bearskin hat and shouted "Forward." Napoleon, displaying his characteristic decisiveness, rebuked the soldier, stating, "Only a beardless youth would presume to judge in advance what I should do"
III. Political Reforms:
Napoleon's impact extended beyond the battlefield to the world of domestic policies and governance, where he instituted significant reforms that left a lasting mark on France. Central to his domestic agenda was the creation of the Napoleonic Code in 1804.
This legal framework sought to unify and codify French law, emphasizing principles of equality, property rights, and individual freedoms. The Napoleonic Code became a cornerstone of modern legal systems, influencing civil law jurisdictions worldwide. For a more detailed examination of the Napoleonic Code, you can refer to Britannica.
In addition to legal reforms, Napoleon implemented a series of administrative changes aimed at streamlining and modernizing the French state. He established the Prefect system, appointing Prefects to oversee regional governance and implement policies. This decentralized administrative structure aimed to maintain order and facilitate efficient governance across different regions of France.
Napoleon's focus on meritocracy was evident in his approach to education and career advancement. The establishment of lycées, secondary schools that emphasized rigorous academic standards, aimed to produce a cadre of well-educated individuals loyal to the state. This emphasis on education contributed to the development of a skilled bureaucracy that played a crucial role in the functioning of the Napoleonic state.
Furthermore, Napoleon's economic policies aimed at stabilizing and revitalizing the French economy. He introduced the Continental System, an economic blockade against British trade, in an attempt to weaken the British economy and enhance French economic self-sufficiency. However, this policy faced challenges and ultimately contributed to tensions within and outside of France (source)
In exploring Napoleon's political reforms, one encounters a complex legacy of legal innovations, administrative restructuring, and economic initiatives. While some aspects of his domestic policies laid the foundation for modern governance, others sparked debates about the balance between centralization and individual liberties. This intricate narrative invites reflection on the enduring impact of Napoleon's vision on the shaping of French society and its legal and administrative structures.
IV. Imperial Expansion:
Napoleon's imperial expansion marked a significant chapter in European history, characterized by strategic annexations and diplomatic alliances that reshaped the map of the continent. His vision for a dominant French Empire led to the annexation of various territories, extending French influence across Europe. Utilizing a combination of military might and political cunning, Napoleon sought to consolidate power and forge alliances that aligned with his imperial ambitions.
The map of Europe underwent dramatic changes during this period, reflecting Napoleon's dynamic approach to expansion. Annexations, such as the incorporation of the Italian territories and parts of the Rhineland, showcased his desire to establish a formidable French presence.
The map below provides a visual representation of Napoleon's Empire in 1810, offering a clear depiction of the extent of his territorial control during that time (source):
Simultaneously, strategic alliances, like the Confederation of the Rhine, played a crucial role in maintaining control over conquered regions and securing support from key allies.
This visual representation can offer readers a clear overview of the evolving landscape during this era of imperial expansion, enhancing their understanding of the dynamic geopolitical changes orchestrated by Napoleon.
V. Controversial Decisions:
Controversial decisions marked Napoleon's reign, and among the most notorious events was the Jaffa executions during the Egyptian campaign. This episode, occurring in 1799, involved the alleged poisoning of French soldiers afflicted by the bubonic plague. Napoleon's response was a mass execution of hundreds of prisoners, leading to ethical dilemmas and widespread criticism.
The Jaffa executions present a stark ethical challenge, raising questions about the justifiability of such extreme measures, especially when dealing with a health crisis. Critics argue that Napoleon's decision to resort to mass execution reflects a disregard for human rights and ethical principles. The harshness of this action fueled debates about the morality of military leaders in times of crisis, exploring the boundaries of acceptable conduct even in the midst of war.
Furthermore, the Jaffa executions became a focal point for critics of Napoleon's regime, both during and after his rule. The event contributed to a growing perception of Napoleon as a leader willing to sacrifice human lives for strategic or political gain. The controversy surrounding the executions remains a significant aspect of historical discussions about Napoleon's character and the ethical considerations inherent in wielding military power.
To gain a deeper understanding of this controversial event, you may find the YouTube video "Napoleon’s Greatest Crime?" by Epic History TV insightful. The video explores General Napoleon Bonaparte's actions during his Egyptian expedition, particularly the storming of the Ottoman-held city of Jaffa, and dives into the centuries-long controversy surrounding his decisions. The narration provides valuable context and analysis, shedding light on this historical event.
Video Citation:
Title: Napoleon’s Greatest Crime?
Creator: https://m.youtube.com/@EpichistoryTv
Published: November 2023
In examining these controversial decisions, it is crucial to navigate the complexities of historical judgment, acknowledging the ethical dilemmas faced by leaders while critically assessing the consequences of their actions. The Jaffa executions, in particular, serve as a poignant example of the challenges posed by the intersection of military strategy, ethics, and the pursuit of power.
VI. Downfall and Exile:
Napoleon's downfall and exile marked the culmination of a once-mighty empire's collapse. After a series of defeats, including the decisive Battle of Leipzig in 1813, Napoleon faced increasing pressure from European coalitions. In 1814, Paris fell, compelling him to abdicate the throne and go into exile on the island of Elba.
His first exile was characterized by a sense of uncertainty in European politics as the victorious powers sought to reshape the continent.
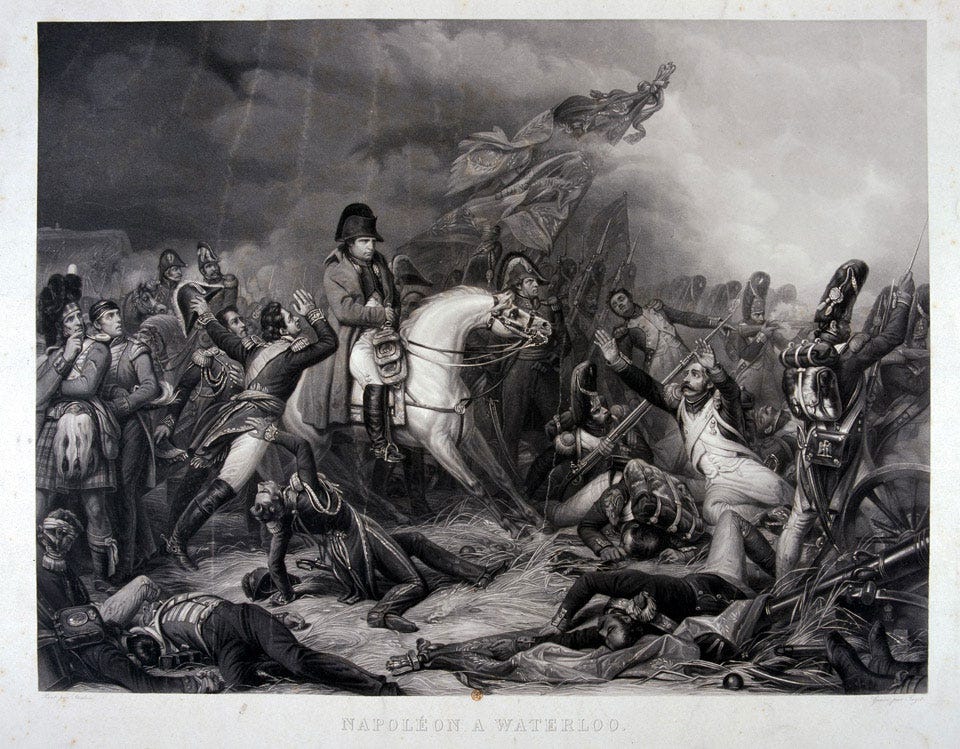
The Hundred Days, a brief period of Napoleon's return to power in 1815, brought both hope and renewed conflict. Escaping from Elba, Napoleon rallied supporters and reclaimed the French throne, prompting a resumption of hostilities. However, his final defeat occurred at the Battle of Waterloo in June 1815. This marked the end of the Napoleonic era as he abdicated once again, paving the way for his second and final exile.
The National Army Museum's deep dive on the Battle of Waterloo offers a comprehensive examination of the engagement, shedding light on the strategic maneuvers, key players, and the profound impact of this historic battle. This resource provides valuable insights into the intricacies of Waterloo, offering a deeper understanding of the events that shaped the course of European history.
Additionally, to visually capture the essence of Napoleon at Waterloo, consider including the mezzotint titled "The Emperor Napoleon on horseback at the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815." This image, published by Jazet and Theodore, Vibert, Bance, and Schroth in 1870, portrays Napoleon's presence on the battlefield during this pivotal moment.
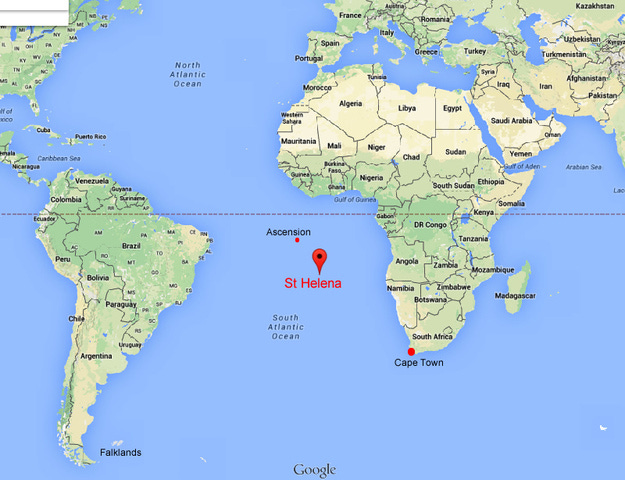
The defeated emperor was subsequently sent to Saint Helena, a remote island in the South Atlantic. The isolation of Saint Helena served as a strategic measure to prevent any further attempts at escape or political maneuvering. Napoleon spent his remaining years on the island until his death in 1821, reflecting on his turbulent legacy and impact on European history. The events of his downfall and exile underscore the complexities of power, ambition, and the consequences of military and political decisions on a global scale.
Map of Saint Helena, the isolated island where Napoleon Bonaparte spent his remaining years in exile.
VII. Legacy and Impact:
Napoleon Bonaparte's legacy on Europe and the world is a multifaceted story, woven with both positive contributions and negative consequences. On the positive side, his Napoleonic Code, a comprehensive legal system, laid the foundation for modern legal frameworks across various nations. This civil law system prioritized equality before the law and protected property rights, influencing legal developments far beyond his era.
However, the wake of Napoleon's military campaigns left a trail of destruction, and his quest for dominance sparked widespread suffering. The Napoleonic Wars, characterized by unprecedented scale and tactics, claimed countless lives and reshaped political boundaries across the continent. His ambitious pursuit of empire-building cast a long shadow over Europe, engendering a climate of fear and uncertainty.
In the midst of the 200th anniversary of Napoleon's death in 2021, the discussion on how to commemorate him renews fervently, as highlighted by Michael Vecchio in his article "Brilliant and Flawed: The Enduring Legacy of Napoleon Bonaparte". Vecchio's exploration navigates the contrasting perspectives surrounding Napoleon, portraying him as a military genius, autocratic despot, progressive visionary, and bloodthirsty war monger. Whether viewed as a hero or a villain, the name Napoleon remains unforgettable.
As we contemplate the complexities of Napoleon's legacy, it's crucial to consider various viewpoints. Some, like historian Andrew Roberts, laud his administrative and legal reforms, attributing positive changes to his rule. On the contrary, critics, such as David A. Bell, emphasize the autocratic nature of his regime and the suppression of liberties. Navigating this historiographical debate is essential to understanding the nuanced legacy of Napoleon Bonaparte, a figure whose imprint on history is both enduring and contested.
To further enrich the exploration of Napoleon's impact, a video titled "Napoleon Bonaparte: The Strategic Genius" by Biographics provides a visual journey into his strategic mind. With 38K likes and over 1.88 million views since its upload on February 19, 2018, this video offers dynamic insights that complement the ongoing discourse on Napoleon's historical significance.
Video Citation:
Title: Napoleon Bonaparte: The Strategic Genius
Creator: https://youtube.com/@Biographics
Published: February 2018
VIII. Conclusion:
Napoleon Bonaparte's rise to power and subsequent fall encapsulates a complex narrative of military brilliance, political acumen, and strategic miscalculations. His legacy remains a subject of historical fascination, leaving an indelible mark on the course of European history. The rise and fall of Napoleon symbolize the interplay between individual agency and the forces of history, illustrating the highs and lows of one of the most iconic figures of the 19th century.